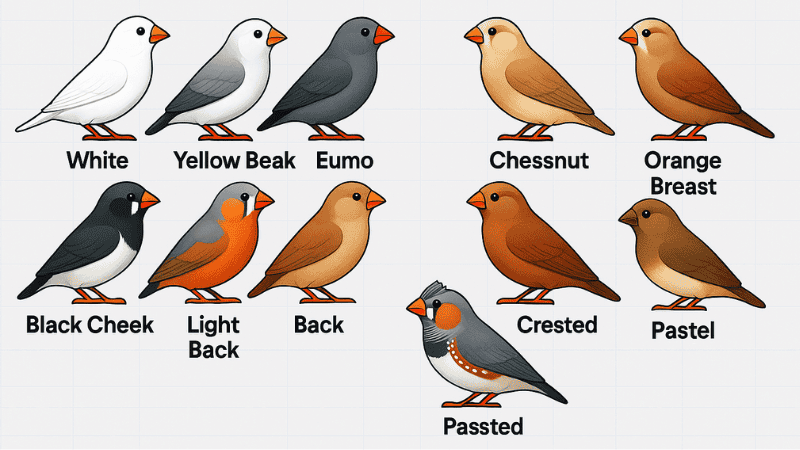
Zebra Finch Mutation Calculator
Male Finch
Female Finch
Offspring Visuals
(Representative images above, all possible outcomes with images in the table below)
Possible Offspring
| Image | Sex | Probability | Variations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Select parent mutations and click calculate. | |||
Zebra finches are fascinating birds, and their many color forms and varieties, known as mutations, make them a popular choice for breeders. Understanding how these mutations are passed down can seem tricky, but a zebra finch mutation calculator can make it much easier. This guide will give you the basics you need to know.
The Basics of Zebra Finch Genetics
Zebra finch mutations can seem complicated, but they follow basic rules of genetics, similar to how traits are passed down in other animals (including humans!). Here’s a simple breakdown:
The Basics: Genes and Alleles
Think of genes as instructions for specific traits, like feather color or pattern. Each bird has two copies of each gene, one from its father and one from its mother. These copies are called alleles.
Mutations are simply changes in these genes (alleles) that result in a different appearance or trait.
How Traits Are Inherited
The most common ways mutations are inherited in zebra finches are:
- Recessive: For a bird to show a recessive mutation (like White or Black Cheek), it needs to inherit two copies of the mutated allele – one from each parent. If it only inherits one copy, it won’t show the mutation but will be a “split” for it, meaning it carries the gene and can pass it on to its offspring.
- Example: If a bird is “split for White,” it carries one White allele but looks Normal. If it mates with another bird that is also “split for White” or is a visual White, they can produce White offspring.
- Dominant: For a bird to show a dominant mutation (like Crested or Black Face), it only needs to inherit one copy of the mutated allele from either parent.
- Example: A bird with one Crested allele will have a crest.
- Sex-linked: These mutations (like Fawn or Light Back) are carried on the sex chromosomes. In zebra finches, males have two Z chromosomes (ZZ), and females have one Z and one W chromosome (ZW).
- Males need two copies of a sex-linked recessive mutation allele (one on each Z chromosome) to show the trait, or one copy if the mutation is sex-linked dominant (less common). They can be “split” if they have one mutated allele and one normal allele on their Z chromosomes.
- Females only have one Z chromosome, so if they inherit a sex-linked mutation allele on their Z chromosome, they will show the trait (they cannot be “split” for sex-linked recessive traits in the same way males can).
Understanding Genotype and Phenotype
- Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of a bird – the specific alleles it carries.
- Phenotype refers to the observable traits of a bird – what it actually looks like.
A mutation calculator helps you connect the genotype of your birds to the possible phenotypes of their offspring.
Using a Mutation Calculator
A mutation calculator helps you predict the probability of getting certain mutations in the offspring based on the known mutations of the parent birds. By selecting the mutations each parent bird has (including if they are “split” for recessive traits), the calculator uses genetic principles to show you the possible outcomes and how likely they are.
It’s a valuable tool for breeders to understand the potential results of pairing different birds and to work towards specific color or pattern goals.
Remember, genetics involves chance, so the calculator shows probabilities, not guarantees for any single clutch of eggs. However, over many offspring, the results tend to align with the predicted probabilities.
How to Use the Zebra Finch Mutation Calculator
This calculator helps you predict the possible mutations and their probabilities in the offspring of a male and female Zebra Finch pair. Follow these simple steps:
Step 1: Select Mutations for the Male Finch
- Look at the “Male Finch” section on the left side of the calculator.
- You will see groups for Recessive Factors, Dominant Factors, and Sex-linked Factors.
- Within each group, click on the dropdown header (e.g., “Select Recessive Mutations”).
- A list of available mutations will appear.
- Check the box next to each mutation that your Male Finch visually displays OR is “split” for (if applicable, like recessive or sex-linked splits).
- You can select multiple mutations in each category.
- Click the dropdown header again to close the list. The selected mutations will be listed below the dropdown.
Step 2: Select Mutations for the Female Finch
- Move to the “Female Finch” section in the middle.
- Similar to the male section, you’ll find groups for Recessive, Dominant, and Sex-linked Factors.
- Click the dropdown header for each group.
- Check the box next to each mutation that your Female Finch visually displays or is “split” for (remembering that females cannot be split for sex-linked recessive traits).
- Close the dropdowns once you’ve made your selections. The selected mutations will be listed below the dropdown.
Step 3: Calculate Offspring
- Once you have selected the mutations for both the Male and Female Finches, click the “Calculate Offspring” button located below the input sections.
Step 4: View Results
- The calculator will process the genetic information and display the results in the “Possible Offspring” section at the bottom.
- The results are shown in a table with the following columns:
- Image: A representative image of the predicted offspring phenotype (if available).
- Sex: Indicates if the outcome is for Male, Female, or Both sexes (if the mutation is not sex-linked).
- Probability: The percentage chance of an offspring inheriting this specific combination of mutations.
- Variations: A list of the mutations that make up this specific offspring phenotype.
Step 5: Review Offspring Visuals
- Above the results table, in the “Offspring Visuals” section, you may see representative images for the most probable male and female offspring phenotypes based on your selections.
That’s it! You can change the selected mutations for the parent birds at any time and click “Calculate Offspring” again to see new results.
Probability in Bird Breeding: Understanding the Odds
Zebra finch mutation calculators use the principles of Mendelian genetics to determine the likelihood of different genetic outcomes. By understanding the inheritance patterns of each mutation (recessive, dominant, or sex-linked), the calculator predicts the percentage chance of offspring inheriting specific combinations of these genes. This helps breeders visualize the potential results of different pairings and plan their breeding strategies accordingly.
Conclusion
A zebra finch mutation calculator is a powerful yet simple tool for anyone breeding these colorful birds. By taking the guesswork out of genetics, it allows breeders to make informed decisions, understand the probabilities of different outcomes, and ultimately work towards creating the specific and beautiful zebra finch varieties they desire.